Client invoke Program
- Introduction
- Solana Program Review
- A client-side script to invoke a program
- A NextJS frontend application to invoke the program
- React Query Basics
- Refs
Introduction
In this article, we will learn how to interact with Solana programs from both client-side scripts and frontend applications like React. We'll explore different approaches to sending transactions and invoking program instructions, with a focus on building user-friendly interfaces for your decentralized applications.
First, let's start by going over the basic structure of Anchor's TypeScript library. The primary object you'll be using is the Program object. A Program instance represents a specific Solana program and provides a custom API for reading and writing to the program.
To create an instance of Program, you'll need the following:
IDL- file representing the structure of a programConnection- the cluster connectionWallet- default keypair used to pay for and sign transactionsProvider- encapsulates theConnectionto a Solana cluster and aWallet
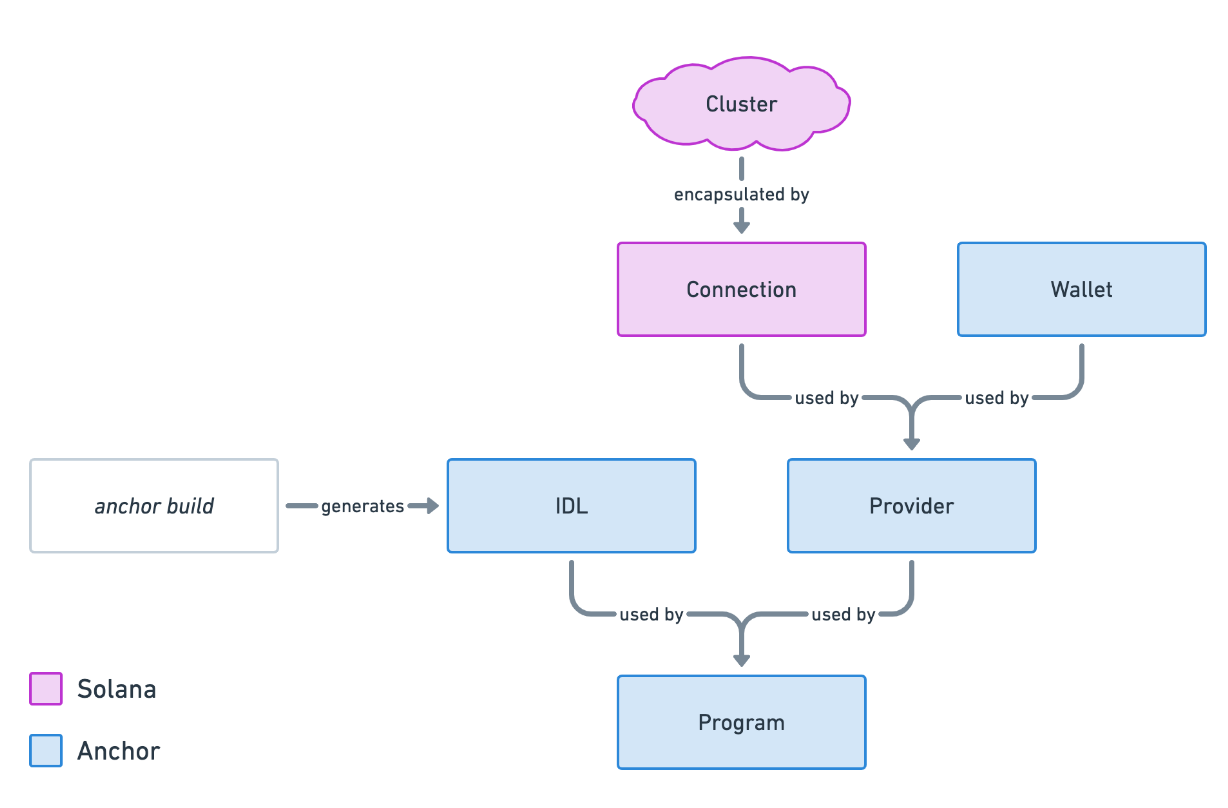
When building applications on Solana, there are several approaches to invoke a program and interact with the blockchain:
- Use the
@solana/web3.jslibrary to directly create transactions and instructions - Use the
anchor-clientlibrary to invoke the program - In frontend applications like React, use the
useAnchorWallethook from@solana/wallet-adapter-reactto connect to a wallet and invoke the program
Now, let's see how to invoke a program in frontend applications like React.
Solana Program Review
Before we start, let's review the program code.
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { #[program] pub mod solanapda { use anchor_lang::solana_program::entrypoint::ProgramResult; use super::*; pub fn create(ctx: Context<Create>, name: String) -> ProgramResult { let bank = &mut ctx.accounts.bank; // set the name of the bank to the one passed in bank.name = name; // set the balance to 0 bank.balance = 0; // set the owner to the user, who pay for the creation of the bank account bank.owner = ctx.accounts.user.key(); msg!("Bank ({:?}) account ({:?}) created", bank.name, bank.key()); Ok(()) } #[derive(Accounts)] #[instruction(name: String)] pub struct Create<'info> { // #[account(init, payer = user, space = 8 + 32, seeds = [b"bank".as_ref()], bump)] #[account( init, payer = user, space = 8 + Bank::INIT_SPACE, seeds = [ b"bankaccount".as_ref(), user.key().as_ref(), name.as_bytes() ], bump) ] pub bank: Account<'info, Bank>, // the user need to be mutable, so that he can pay for the creation, its wallet balance will be reduced #[account(mut)] // NOTE: user should be mutable // otherwise you will get an error // error: the payer specified for an init constraint must be mutable. // // NOTE: When annotating an account with #[account()], which is not mutable, you will get an error // #[account()] pub user: Signer<'info>, pub system_program: Program<'info, System>, } #[account] #[derive(InitSpace)] pub struct Bank { #[max_len(64)] pub name: String, pub owner: Pubkey, pub balance: u64, } }
The create instruction is the instruction to create a bank account for specific user.
The Create struct is the context of the instruction.
The Create struct defines the accounts required for the create instruction:
-
bank: The bank account to be createdinit- Initialize a new account owned by the programpayer = user- The user pays for account creationspace = 8 + Bank::INIT_SPACE- Allocate space for account data (8 bytes for discriminator + space for Bank struct)seeds = [...]- PDA seeds to derive the account address:- "bankaccount" prefix
- User's public key
- Bank name
bump- Store bump seed for PDA
-
user: The user creating the bank account- Must be mutable (
mut) since they pay for account creation - Must sign the transaction (
Signer)
- Must be mutable (
-
system_program: Required for creating new accounts
The Bank struct is the account of the bank.
The Bank struct represents the data stored in a bank account. It contains:
-
name: A String field with maximum length of 64 bytes- Stores the name of the bank account
- Uses
#[max_len(64)]attribute to limit the string length
-
owner: A Pubkey field- Stores the public key of the account owner
- Set to the user's public key when account is created
-
balance: A u64 field- Tracks the account balance in lamports
- Initialized to 0 when account is created
- Updated by deposit and withdraw instructions
The struct uses #[account] attribute to mark it as an account that can store data on-chain.
The #[derive(InitSpace)] attribute automatically calculates the required space for the account based on its fields.
Ok, now let's start to build a client-side script to invoke the bank program to create a bank account.
A client-side script to invoke a program
1. Create a client-side script
Below is a client-side script to invoke the bank program to create a bank account.
import { Connection, Keypair, PublicKey, SystemProgram } from "@solana/web3.js";
import { Program, AnchorProvider, Wallet, utils } from "@coral-xyz/anchor";
import { homedir } from "os";
import { readFileSync } from "fs";
import path from "path";
import { Command } from "commander";
import type { Solanapda } from "./idl/solanapda"; // 你的类型定义
import idl from "./idl/solanapda.json";
import { getKeypairFromFile } from "@solana-developers/helpers";
// configure command line options
const program = new Command();
program
.name("create-bank")
.description("Create a new bank account")
.option("-n, --name <string>", "bank name", "CLI Bank")
.option(
"-N, --network <string>",
"solana network (devnet or localhost)",
"localhost"
)
.parse(process.argv);
const options = program.opts();
// helper function to load keypair from file
const loadKeypairFromFile = (filePath: string): Keypair => {
const expanded = filePath.replace("~", homedir());
const secretKey = new Uint8Array(JSON.parse(readFileSync(expanded, "utf-8")));
return Keypair.fromSecretKey(secretKey);
};
async function initializeConnection() {
const endpoint =
options.network === "devnet"
? "https://api.devnet.solana.com"
: "http://localhost:8899";
const connection = new Connection(endpoint, "confirmed");
// NOTE: We can use custom function to load keypair from file or use build in
// function to load keypair from file
//
// const wallet = loadKeypairFromFile("~/.config/solana/id.json");
// use build int function to load keypair from file
// Source: https://github.com/solana-developers/helpers/blob/main/src/lib/keypair.ts
// Source: https://github.com/solana-developers/helpers/blob/af00163b866c44cc93a1fa64e2f8189366d39dce/src/lib/keypair.ts#L11
const wallet = await getKeypairFromFile();
console.log("Using wallet:", wallet.publicKey.toString());
console.log("Network:", options.network);
const provider = new AnchorProvider(
connection,
new Wallet(wallet),
AnchorProvider.defaultOptions()
);
return { provider, wallet };
}
async function createBank(
program: Program<Solanapda>,
wallet: Keypair,
name: string
) {
// Generate PDA
// The seeds of PDA is a combination of the program id, the user's public key, and the bank name
const [bankPDA] = PublicKey.findProgramAddressSync(
[
utils.bytes.utf8.encode("bankaccount"),
wallet.publicKey.toBytes(),
utils.bytes.utf8.encode(name), // Add bank name as seed
],
program.programId
);
console.log("Bank PDA:", bankPDA.toString());
// Send create transaction
console.log(`Creating bank with name: ${name} ...`);
const tx = await program.methods
.create(name)
.accounts({
user: wallet.publicKey,
})
.rpc();
// Wait for transaction confirmation
const latestBlockhash =
await program.provider.connection.getLatestBlockhash();
await program.provider.connection.confirmTransaction({
signature: tx,
blockhash: latestBlockhash.blockhash,
lastValidBlockHeight: latestBlockhash.lastValidBlockHeight,
});
console.log("Success! Transaction signature:", tx);
// You can also add a short delay to ensure the account data is available
// await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 2000));
return bankPDA;
}
async function fetchBankInfo(program: Program<Solanapda>, bankPDA: PublicKey) {
const bankAccount = await program.account.bank.fetch(bankPDA);
console.log("Bank account data:", {
name: bankAccount.name,
balance: bankAccount.balance.toString(),
owner: bankAccount.owner.toString(),
});
return bankAccount;
}
async function main() {
try {
// 1. Initialize connection
const { provider, wallet } = await initializeConnection();
const program = new Program(idl as Solanapda, provider);
// 2. Create bank account
const bankPDA = await createBank(program, wallet, options.name);
// 3. Fetch bank account info
await fetchBankInfo(program, bankPDA);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error:", error);
process.exit(1);
}
}
main();
2. Explain the code
Let's explain the code step by step based on the solana program review.
Let's break down the key components of this client code:
-
createBankfunction:- Takes a program instance, wallet keypair, and bank name as parameters
- Generates a PDA (Program Derived Address) using 3 seeds:
- "bankaccount" string
- User's public key
- Bank name
- Matches the seeds used in the program's
Createstruct:#![allow(unused)] fn main() { #[account( init, payer = user, space = 8 + Bank::INIT_SPACE, seeds = [ b"bankaccount".as_ref(), user.key().as_ref(), name.as_bytes() ], bump) ] } - Calls the program's
createinstruction with the bank name - Waits for transaction confirmation
- Returns the bank PDA for later use
-
fetchBankInfofunction:- Fetches the bank account data using the PDA
- Displays the bank's:
- Name (String)
- Balance (u64)
- Owner (Pubkey)
- These fields match the program's
Bankstruct:#![allow(unused)] fn main() { pub struct Bank { pub name: String, pub owner: Pubkey, pub balance: u64, } }
-
mainfunction flow:- Initializes connection and gets wallet
- Creates program instance with IDL
- Creates new bank account with specified name
- Fetches and displays the bank account info
The client code directly interacts with the on-chain program's instructions and account structures defined in Rust. The PDA generation and account structure in TypeScript must exactly match what's defined in the program for successful interaction.
3. Setup a nodejs environment to run the script
We can setup a nodejs environment to run the script.
#!/bin/bash
# Colors for output
GREEN='\033[0;32m'
RED='\033[0;31m'
NC='\033[0m' # No Color
echo -e "${GREEN}Setting up Node.js environment...${NC}"
# Check if Node.js is installed
if ! command -v node &> /dev/null; then
echo -e "${RED}Node.js is not installed. Please install Node.js first.${NC}"
exit 1
fi
# Create project directory if it doesn't exist
mkdir -p solana-bank-client
cd solana-bank-client
# Initialize npm project if package.json doesn't exist
if [ ! -f package.json ]; then
echo -e "${GREEN}Initializing npm project...${NC}"
pnpm init -y
fi
# Install dependencies
echo -e "${GREEN}Installing dependencies...${NC}"
pnpm install --save \
@solana/web3.js \
@coral-xyz/anchor \
@solana-developers/helpers \
typescript \
ts-node \
commander \
@types/node
# Create tsconfig.json if it doesn't exist
if [ ! -f tsconfig.json ]; then
echo -e "${GREEN}Creating TypeScript configuration...${NC}"
cat > tsconfig.json << EOF
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es2020",
"module": "commonjs",
"strict": true,
"esModuleInterop": true,
"skipLibCheck": true,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true,
"resolveJsonModule": true
}
}
EOF
fi
# Check if create-bank.ts exists in the current directory
if [ ! -f create-bank.ts ]; then
echo -e "${RED}Please create create-bank.ts file with your code first${NC}"
exit 1
fi
# Run the code
echo -e "${GREEN}Running the code...${NC}"
npx ts-node create-bank.ts
3. Prepare the IDL and type files
The script needs the IDL and type files which are generated when building the Anchor program. Make sure you've run anchor build in your program directory first. This will generate:
- The IDL file at
target/idl/your_program.json - TypeScript types at
target/types/your_program.ts
You'll need to copy or reference these files in your client directory to interact with the program.
In our case, the IDL file is target/idl/solanapda.json and the type file is target/types/solanapda.ts.
4. Run the script
Now, save the code to a file, for example, create-bank.ts, and run the script.
npx ts-node create-banks.ts --name "Rich Bank"
(node:82552) [DEP0040] DeprecationWarning: The `punycode` module is deprecated. Please use a userland alternative instead.
(Use `node --trace-deprecation ...` to show where the warning was created)
Using wallet: FCxBXdduz9HqTEPvEBSuFLLAjbVYh9a5ZgEnZwKyN2ZH
Network: localhost
Bank PDA: EYxqs3ZHCG5j8DYaZvYKtwDSxbkCn2jgLYvK7cpksimq
Creating bank with name: Rich Bank ...
Success! Transaction signature: 5qcf5Puu6Vw3kVNDsqKSqVjanYwBqxcD6qVk6BzrnzVgvwecdjGPYvJeLrLPhkaCzUoMTdBii47XXtL8edpDu8i7
Bank account data: {
name: 'Rich Bank',
balance: '0',
owner: 'FCxBXdduz9HqTEPvEBSuFLLAjbVYh9a5ZgEnZwKyN2ZH'
}
Great! We can see that the bank account is created successfully.
A NextJS frontend application to invoke the program
Although we can setup a nextjs project and use the @solana/wallet-adapter-react to invoke the program, but it's not the best way to do it.
We can leverage npx create-solana-dapp to create a nextjs project and use the @solana/wallet-adapter-react to invoke the program. This will skip the tedious steps of scaffolding the project(like creating the layout, components, especially wallet adapter, etc.) and focus on the core logic.
npx create-solana-dapp@latest solana-dapp-example -t next-tailwind-counter --pnpm
# Available templates:
# next-tailwind-counter
# next-tailwind-basic
# next-tailwind
#
# NOTE: There's no --typescript/--eslint/--tailwind option in the latest version of create-solana-dapp
# npx create-solana-dapp@latest --typescript --eslint --tailwind --pnpm
# add dependencies
pnpm install \
@coral-xyz/anchor \
@solana/web3.js \
@solana/wallet-adapter-react \
@solana/wallet-adapter-react-ui \
@solana/wallet-adapter-base \
@solana/wallet-adapter-wallets
After creating the project, we need to replace all solanadappexample with bank in the project.
We can add a new tab called Bank in the navigation bar.
If you are lazy like me, you can use a script to replace all solanadappexample with bank in the project.
function copy() {
# Use rsync to properly sync directories
rsync -a --delete ./src/components/solanadappexample/ ./src/components/bank
rsync -a --delete ./src/app/solanadappexample/ ./src/app/bank
cp -f ./anchor/src/solanadappexample-exports.ts ./anchor/src/bank-exports.ts
}
function copy_using_cp() {
# NOTE: This is not a good idea to use cp to copy directories.
# If you run it multiple times, it will create new bank folder in existing bank folder.
cp -rf ./src/components/solanadappexample ./src/components/bank
cp -rf ./src/app/solanadappexample ./src/app/bank
cp ./anchor/src/solanadappexample-exports.ts ./anchor/src/bank-exports.ts
}
# replace all solanadappexample with bank in components
function replace_in_components() {
cd ./src/components/bank
rg Solanadappexample --files-with-matches | xargs sed -i '' "s/Solanadappexample/Bank/g"
rg solanadappexample --files-with-matches | xargs sed -i '' "s/solanadappexample/bank/g"
rg SOLANADAPPEXAMPLE --files-with-matches | xargs sed -i '' "s/SOLANADAPPEXAMPLE/BANK/g"
cd -
}
# replace
function replace_in_exports() {
bank_export_file="./anchor/src/bank-exports.ts"
# cp ./anchor/src/solanadappexample-exports.ts $bank_export_file
rg Solanadappexample --files-with-matches $bank_export_file | xargs sed -i '' "s/Solanadappexample/Bank/g"
rg solanadappexample --files-with-matches $bank_export_file | xargs sed -i '' "s/solanadappexample/bank/g"
rg SOLANADAPPEXAMPLE --files-with-matches $bank_export_file | xargs sed -i '' "s/SOLANADAPPEXAMPLE/BANK/g"
}
# replace all solanadappexample with bank in components
function replace_in_pages() {
cd ./src/app/bank
rg Solanadappexample --files-with-matches | xargs sed -i '' "s/Solanadappexample/Bank/g"
rg solanadappexample --files-with-matches | xargs sed -i '' "s/solanadappexample/bank/g"
rg SOLANADAPPEXAMPLE --files-with-matches | xargs sed -i '' "s/SOLANADAPPEXAMPLE/BANK/g"
cd -
}
# rename all files in solanadappexample to bank in the IDL file
function rename_files_in_components() {
# rename all files names in src/components/solanadappexample begins with solanadappexample to bank
cd ./src/components/bank
# rename all files names in src/components/solanadappexample begins with solanadappexample to bank
# not file contents!!!
# NOTE: This does not work in fish shell. You have to use bash.
for file in solanadappexample*; do mv "$file" "${file/solanadappexample/bank}"; done
# For fish shell
# for file in solanadappexample*; mv "$file" "${file/solanadappexample/bank}"; end
cd -
}
# add export * from './bank' in the index.ts file
function add_export_in_index_ts() {
# Check if the export line already exists to make it idempotent
if ! grep -q "export \* from './bank-exports'" ./anchor/src/index.ts; then
echo "export * from './bank-exports'" >> ./anchor/src/index.ts
fi
}
copy
replace_in_components
replace_in_exports
replace_in_pages
rename_files_in_components
add_export_in_index_ts
Next, open src/app/layout.tsx and add a /bank link to the links array.
import "./globals.css";
import { ClusterProvider } from "@/components/cluster/cluster-data-access";
import { SolanaProvider } from "@/components/solana/solana-provider";
import { UiLayout } from "@/components/ui/ui-layout";
import { ReactQueryProvider } from "./react-query-provider";
export const metadata = {
title: "solana-dapp-example",
description: "Generated by create-solana-dapp",
};
const links: { label: string; path: string }[] = [
{ label: "Account", path: "/account" },
{ label: "Clusters", path: "/clusters" },
{ label: "Solanadappexample Program", path: "/solanadappexample" },
{ label: "Bank Program", path: "/bank" }, // 🙋🙋🙋🙋🙋, This is the new link
];
export default function RootLayout({
children,
}: {
children: React.ReactNode;
}) {
return (
<html lang="en">
<body>
<ReactQueryProvider>
<ClusterProvider>
<SolanaProvider>
<UiLayout links={links}>{children}</UiLayout>
</SolanaProvider>
</ClusterProvider>
</ReactQueryProvider>
</body>
</html>
);
}
As anchor needs the IDL file and the type file, we can copy the IDL file to target/idl and the type file to target/types. We can obtain them by running anchor build in your program directory first.
In our case, the IDL file is target/idl/solanapda.json and the type file is target/types/solanapda.ts.
We also need to replace the program id in function getBankProgramId with our program id (i.e E5U58NJgCMwtyv3TPaZtoZPmnxUY9vCGrXDMjPpbxm4z).
// Here we export some useful types and functions for interacting with the Anchor program.
import { AnchorProvider, Program } from "@coral-xyz/anchor";
import { Cluster, PublicKey } from "@solana/web3.js";
import BankIDL from "../target/idl/bank.json";
import type { Solanapda as Bank } from "../target/types/bank";
// Re-export the generated IDL and type
export { Bank, BankIDL };
// The programId is imported from the program IDL.
export const BANK_PROGRAM_ID = new PublicKey(BankIDL.address);
// This is a helper function to get the Bank Anchor program.
export function getBankProgram(provider: AnchorProvider, address?: PublicKey) {
return new Program(
{
...BankIDL,
address: address ? address.toBase58() : BankIDL.address,
} as Bank,
provider
);
}
// This is a helper function to get the program ID for the Bank program depending on the cluster.
export function getBankProgramId(cluster: Cluster) {
switch (cluster) {
case "devnet":
case "testnet":
// This is the program ID for the Bank program on devnet and testnet.
return new PublicKey("E5U58NJgCMwtyv3TPaZtoZPmnxUY9vCGrXDMjPpbxm4z");
case "mainnet-beta":
default:
return BANK_PROGRAM_ID;
}
}
Next, let's look at the UI implementation where we'll create components to interact with our Solana program. As we are using @solana/wallet-adapter-react, we can use the WalletMultiButton to connect their wallet.
Luckily, create-solana-dapp has already created the WalletMultiButton for us. We can focus on the logic part.
Let's examine our bank components, which are organized into the following key files:
bank-feature.tsxbank-ui.tsxbank-data-access.tsx
This project structure follows a modular pattern commonly used in create-solana-dapp, with components organized into three main types:
-
*-feature.tsx: The top-level component that serves as the main page or feature. It handles the overall layout and composition of UI components while managing high-level application state. For example,bank-feature.tsxcombines wallet connection state with bank-specific components. -
*-ui.tsx: Contains the presentational components that render the actual UI elements. These components focus purely on display logic and user interactions, receiving data and callbacks as props. For example,bank-ui.tsxhas components likeBankListandBankCreatethat render the bank interface. -
*-data-access.tsx: Manages data fetching, state management, and program interactions. This layer abstracts away the complexity of working with Solana programs and provides clean hooks/interfaces for the UI layer. For example,bank-data-access.tsxwould contain hooks likeuseBankProgramto interact with the on-chain program.
The data-access layer uses React Query to efficiently manage server state and program interactions. Here's how it's structured:
-
Custom hooks that wrap React Query's useQuery and useMutation:
- useQuery for fetching data like account info and balances
- useMutation for program instructions like deposit/withdraw
-
Program account queries:
- Fetch program metadata
- Get list of all bank accounts
- Get individual account details
-
Transaction mutations:
- Create new bank account
- Deposit funds
- Withdraw funds
- Close account
React Query handles important features like:
- Automatic background refreshing
- Cache management
- Loading/error states
- Optimistic updates
- Request deduplication
This pattern keeps program interaction logic isolated from UI components while providing a clean, reactive interface for accessing on-chain data.
This separation of concerns makes the code more maintainable and testable, while keeping the program interaction logic cleanly separated from the UI implementation.
bank-feature.tsx
Let me walk you through the main Bank feature component that brings everything together. This is where all our UI pieces and program interactions come together to create the full banking experience. Take a look at the code in bank-feature.tsx, I'll explain what's happening:
"use client";
import { useWallet } from "@solana/wallet-adapter-react";
import { WalletButton } from "../solana/solana-provider";
import { AppHero, ellipsify } from "../ui/ui-layout";
import { ExplorerLink } from "../cluster/cluster-ui";
import { useBankProgram } from "./bank-data-access";
import { BankCreate, BankList } from "./bank-ui";
export default function BankFeature() {
const { publicKey } = useWallet();
const { programId } = useBankProgram();
return publicKey ? (
<div>
<AppHero
title="Bank"
subtitle={
'Create a new account by clicking the "Create" button. The state of a account is stored on-chain and can be manipulated by calling the program\'s methods (increment, decrement, set, and close).'
}
>
<p className="mb-6">
<ExplorerLink
path={`account/${programId}`}
label={ellipsify(programId.toString())}
/>
</p>
<BankCreate />
</AppHero>
<BankList />
</div>
) : (
<div className="max-w-4xl mx-auto">
<div className="hero py-[64px]">
<div className="hero-content text-center">
<WalletButton />
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}
The code is straightforward, using the useWallet() hook to check if a wallet is connected. If no wallet is connected, it shows a wallet connect button. Once connected, it displays the main bank interface with the program ID, a create account button, and list of existing bank accounts. The useBankProgram() hook provides access to the program ID and other program-related functionality that we defined earlier.
The component is organized into two main sections:
- The hero section with program info and account creation
- The list of existing bank accounts
This clean separation makes the code easy to understand and maintain. Each piece handles a specific responsibility - wallet connection, program interaction, or UI display.
bank-ui.tsx
Next, let's look at the BankCreate BankCard and BankList components, which are located in bank-ui.tsx.
"use client";
import { Keypair, PublicKey } from "@solana/web3.js";
import { useMemo, useState } from "react";
import { ellipsify } from "../ui/ui-layout";
import { ExplorerLink } from "../cluster/cluster-ui";
import { useBankProgram, useBankProgramAccount } from "./bank-data-access";
import toast from "react-hot-toast";
import { useWallet } from "@solana/wallet-adapter-react";
export function BankCreate() {
const { initialize } = useBankProgram();
const [bankName, setBankName] = useState("");
const { publicKey } = useWallet();
return (
<div className="flex gap-2 items-center justify-center">
<input
type="text"
placeholder="Enter bank name"
className="input input-bordered"
value={bankName}
onChange={(e) => setBankName(e.target.value)}
/>
<button
className="btn btn-xs lg:btn-md btn-primary"
onClick={() => {
if (!publicKey) {
toast.error("Please connect your wallet");
return;
}
if (!bankName.trim()) {
toast.error("Please enter a bank name");
return;
}
initialize
.mutateAsync({ name: bankName.trim(), owner: publicKey })
.then(() => setBankName(""));
}}
disabled={initialize.isPending || !publicKey}
>
Create {initialize.isPending && "..."}
</button>
</div>
);
}
function BankCard({
account,
timestamp,
}: {
account: PublicKey;
timestamp: number;
}) {
const { accountQuery } = useBankProgramAccount({ account });
const balance = useMemo(
() => accountQuery.data?.balance ?? 0,
[accountQuery.data?.balance]
);
const name = useMemo(
() => accountQuery.data?.name ?? "Unnamed Bank",
[accountQuery.data?.name]
);
return accountQuery.isLoading ? (
<span className="loading loading-spinner loading-lg"></span>
) : (
<div className="card card-bordered border-base-300 border-4 text-neutral-content">
<div className="card-body items-center text-center">
<div className="space-y-6">
<h2 className="card-title justify-center text-3xl">{name}</h2>
<p className="text-2xl">Balance: {balance.toString()} lamports</p>
<div className="card-actions justify-around">
<button className="btn btn-xs lg:btn-md btn-outline">
Deposit
</button>
<button
className="btn btn-xs lg:btn-md btn-outline"
onClick={() => {
const value = window.prompt(
"Set balance to:",
balance.toString() ?? "0"
);
if (
!value ||
parseInt(value) === balance ||
isNaN(parseInt(value))
) {
return;
}
}}
>
Set
</button>
<button className="btn btn-xs lg:btn-md btn-outline">
Withdraw
</button>
</div>
<div className="flex justify-between items-center gap-2">
<ExplorerLink
path={`account/${account}`}
label={ellipsify(account.toString())}
/>
<button className="btn btn-xs lg:btn-md btn-outline btn-error">
Close
</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}
export function BankList() {
const { accounts, getProgramAccount } = useBankProgram();
if (getProgramAccount.isLoading) {
return <span className="loading loading-spinner loading-lg"></span>;
}
if (!getProgramAccount.data?.value) {
return (
<div className="alert alert-info flex justify-center">
<span>
Program account not found. Make sure you have deployed the program and
are on the correct cluster.
</span>
</div>
);
}
return (
<div className={"space-y-6"}>
{accounts.isLoading ? (
<span className="loading loading-spinner loading-lg"></span>
) : accounts.data?.length ? (
<div className="grid md:grid-cols-2 gap-4">
{accounts.data
?.sort((a, b) => b.timestamp - a.timestamp)
.map((account) => (
<BankCard
key={account.publicKey.toString()}
account={account.publicKey}
timestamp={account.timestamp}
/>
))}
</div>
) : (
<div className="text-center">
<h2 className={"text-2xl"}>No accounts</h2>
No accounts found. Create one above to get started.
</div>
)}
</div>
);
}
The code above shows three React components that interact with a Solana program using Anchor:
BankCreate - A form component that allows users to create new bank accounts by invoking the program's create instruction. It handles user input and transaction submission.
BankCard - A component that displays details for a single bank account, showing information like the public key and timestamp. It receives account data as props.
BankList - The main component that fetches and displays all bank accounts. It:
- Uses the
useBankProgramhook to access program accounts - Shows loading states while data is being fetched
- Displays an info message if the program isn't found
- Renders a grid of
BankCardcomponents for each account - Shows a message when no accounts exist
- Sorts accounts by timestamp
Together these components provide a full UI for interacting with the Solana program - creating new accounts and viewing existing ones.
bank-data-access.tsx
Finally, let's look at the data access layer, which is located in bank-data-access.tsx.
"use client";
import { getBankProgram, getBankProgramId } from "@project/anchor";
import { useConnection } from "@solana/wallet-adapter-react";
import { Cluster, Keypair, PublicKey } from "@solana/web3.js";
import { useMutation, useQuery } from "@tanstack/react-query";
import { useMemo } from "react";
import toast from "react-hot-toast";
import { useCluster } from "../cluster/cluster-data-access";
import { useAnchorProvider } from "../solana/solana-provider";
import { useTransactionToast } from "../ui/ui-layout";
export function useBankProgram() {
const { connection } = useConnection();
const { cluster } = useCluster();
const transactionToast = useTransactionToast();
const provider = useAnchorProvider();
const programId = useMemo(
() => getBankProgramId(cluster.network as Cluster),
[cluster]
);
const program = useMemo(
() => getBankProgram(provider, programId),
[provider, programId]
);
const accounts = useQuery({
queryKey: ["bank", "all", { cluster }],
// queryFn: () => program.account.bank.all(),
queryFn: async () => {
const accounts = await program.account.bank.all();
const accountsWithTimestamp = await Promise.all(
accounts.map(async (account) => {
const signatures = await connection.getSignaturesForAddress(
account.publicKey,
{ limit: 1 }
);
return {
...account,
timestamp: signatures[0]?.blockTime || 0,
};
})
);
return accountsWithTimestamp.sort((a, b) => b.timestamp - a.timestamp);
},
});
const getProgramAccount = useQuery({
queryKey: ["get-program-account", { cluster }],
queryFn: () => connection.getParsedAccountInfo(programId),
});
const initialize = useMutation({
mutationKey: ["bank", "initialize", { cluster }],
// mutationFn: ({ keypair, name }: { keypair: Keypair; name: string }) =>
mutationFn: async ({ name, owner }: { name: string; owner: PublicKey }) =>
program.methods
.create(name)
.accounts({
user: owner,
})
// .signers([keypair])
.rpc(),
onSuccess: (signature) => {
transactionToast(signature);
return accounts.refetch();
},
onError: () => toast.error("Failed to initialize account"),
});
return {
program,
programId,
accounts,
getProgramAccount,
initialize,
};
}
export function useBankProgramAccount({ account }: { account: PublicKey }) {
const { cluster } = useCluster();
const transactionToast = useTransactionToast();
const { program, accounts } = useBankProgram();
const accountQuery = useQuery({
queryKey: ["bank", "fetch", { cluster, account }],
queryFn: () => program.account.bank.fetch(account),
});
return {
accountQuery,
};
}
Let me explain the bank-data-access.tsx file in detail:
- Main Hook: useBankProgram
export function useBankProgram() {
// Get necessary context and tools
const { connection } = useConnection(); // Solana connection
const { cluster } = useCluster(); // Current network cluster
const provider = useAnchorProvider(); // Anchor provider
const transactionToast = useTransactionToast(); // Transaction notification tool
// Get program ID and program instance
const programId = useMemo(() => getBankProgramId(cluster.network), [cluster]);
const program = useMemo(() => getBankProgram(provider, programId), [provider, programId]);
- Account Query Functionality
// Query all bank accounts
const accounts = useQuery({
queryKey: ["bank", "all", { cluster }],
queryFn: async () => {
// 1. Get all accounts
const accounts = await program.account.bank.all();
// 2. Add timestamp for each account
const accountsWithTimestamp = await Promise.all(
accounts.map(async (account) => {
const signatures = await connection.getSignaturesForAddress(
account.publicKey,
{ limit: 1 }
);
return {
...account,
timestamp: signatures[0]?.blockTime || 0,
};
})
);
// 3. Sort by timestamp
return accountsWithTimestamp.sort((a, b) => b.timestamp - a.timestamp);
},
});
// Query program account info
const getProgramAccount = useQuery({
queryKey: ["get-program-account", { cluster }],
queryFn: () => connection.getParsedAccountInfo(programId),
});
- Account Creation Functionality
// Mutation for initializing new bank account
const initialize = useMutation({
mutationKey: ["bank", "initialize", { cluster }],
mutationFn: async ({ name, owner }) =>
program.methods.create(name).accounts({ user: owner }).rpc(),
onSuccess: (signature) => {
transactionToast(signature); // Show success notification
return accounts.refetch(); // Refresh account list
},
onError: () => toast.error("Failed to initialize account"),
});
- Single Account Query Hook
export function useBankProgramAccount({ account }: { account: PublicKey }) {
// ... context getters omitted ...
// Query single account data
const accountQuery = useQuery({
queryKey: ["bank", "fetch", { cluster, account }],
queryFn: () => program.account.bank.fetch(account),
});
return { accountQuery };
}
Key Features of this file:
-
Data Access Layer Abstraction
- Encapsulates all Solana program interaction logic
- Provides clean interfaces for UI components
-
React Query Integration
- Uses
useQueryfor read operations (querying accounts) - Uses
useMutationfor write operations (creating accounts) - Automatic handling of caching, loading states, and error handling
- Uses
-
Performance Optimizations
- Uses
useMemoto cache program instances - Implements account timestamp and sorting functionality
- Automatic data refetching to keep UI in sync
- Uses
-
Error Handling
- Integrated toast notification system
- Provides feedback for transaction success and failure
-
Modular Design
- Separates program interaction logic from UI logic
- Provides reusable hooks
- Easy to test and maintain
This design pattern ensures:
- UI components can focus on presentation logic
- Program interaction logic is centrally managed
- Data fetching and caching is unified
- Error handling and user feedback is standardized
React Query Basics
Let me explain React Query and how it's used in this code:
React Query is a powerful library for managing server state in React applications. Think of it as a combination of:
- Data fetching
- Caching
- State management
- Error handling
Key Concepts
- useQuery - For fetching/reading data
// Basic example
const { data, isLoading, error } = useQuery({
queryKey: ['todos'], // Unique identifier for this query
queryFn: fetchTodoList, // Function that returns a promise
});
// Real example from our code
const accounts = useQuery({
queryKey: ["bank", "all", { cluster }],
queryFn: async () => {
const accounts = await program.account.bank.all();
// Add timestamps and sort...
return accountsWithTimestamp;
},
});
// You can then use the data like:
if (accounts.isLoading) return <Loading />;
if (accounts.error) return <Error />;
return <div>{accounts.data.map(account => ...)}</div>;
- useMutation - For updating/writing data
// Basic example
const mutation = useMutation({
mutationFn: (newTodo) => axios.post("/todos", newTodo),
onSuccess: () => {
// Do something after successful mutation
},
});
// Real example from our code
const initialize = useMutation({
mutationFn: async ({ name, owner }) =>
program.methods.create(name).accounts({ user: owner }).rpc(),
onSuccess: (signature) => {
transactionToast(signature); // Show success message
return accounts.refetch(); // Refresh the account list
},
});
// You can then use it like:
<button onClick={() => initialize.mutate({ name: "New Bank", owner })}>
{initialize.isPending ? "Creating..." : "Create Bank"}
</button>;
Key Features
- Automatic Caching
// Data is cached by queryKey
const { data: account } = useQuery({
queryKey: ["bank", "fetch", { cluster, account }],
queryFn: () => program.account.bank.fetch(account),
});
// Second component using same query will use cached data
- Automatic Background Refreshing
const accounts = useQuery({
queryKey: ["bank", "all"],
queryFn: fetchAccounts,
// Optional configuration
refetchInterval: 5000, // Refetch every 5 seconds
staleTime: 30000, // Consider data stale after 30 seconds
});
- Loading & Error States
const { data, isLoading, error } = useQuery({...});
if (isLoading) return <span>Loading...</span>;
if (error) return <span>Error: {error.message}</span>;
return <div>{data.map(item => ...)}</div>;
- Automatic Retries
const query = useQuery({
queryKey: ["data"],
queryFn: fetchData,
retry: 3, // Retry failed requests 3 times
retryDelay: 1000, // Wait 1 second between retries
});
In Our Bank Application
Here's how React Query helps in our bank application:
- Account Listing
// Fetches and caches all bank accounts
const accounts = useQuery({
queryKey: ["bank", "all", { cluster }],
queryFn: async () => {
const accounts = await program.account.bank.all();
// Add timestamps...
return accountsWithTimestamp;
},
});
// Usage in UI
if (accounts.isLoading) return <Loading />;
return (
<div>
{accounts.data?.map((account) => (
<BankCard key={account.publicKey} account={account} />
))}
</div>
);
- Creating New Accounts
// Mutation for creating new accounts
const initialize = useMutation({
mutationFn: async ({ name, owner }) => program.methods.create(name)...,
onSuccess: () => {
accounts.refetch(); // Automatically refresh the account list
},
});
// Usage in UI
<button
onClick={() => initialize.mutate({ name, owner })}
disabled={initialize.isPending}
>
Create Account
</button>
The benefits in our application:
- Automatic caching of account data
- Loading states handled automatically
- Error handling built-in
- Automatic background refreshing
- Optimistic updates
- Consistent data across components
This makes our code much cleaner and more maintainable compared to managing all this state manually with useState and useEffect.
Refs
https://solana.com/docs/programs/anchor/client-typescript
https://lorisleiva.com/create-a-solana-dapp-from-scratch/integrating-with-solana-wallets
https://solana.com/developers/courses/onchain-development/intro-to-anchor-frontend